Your heart is your body’s natural pacemaker, sending electrical signals that regulate its rhythm. However, when this natural system fails, an artificial pacemaker may be required to maintain a regular heartbeat. As a Consultant Interventional Cardiologist in Latur, Dr. Mehul Rathod explains what a pacemaker is, why it's needed, and how it can dramatically improve a patient’s quality of life.
What Is a Pacemaker?
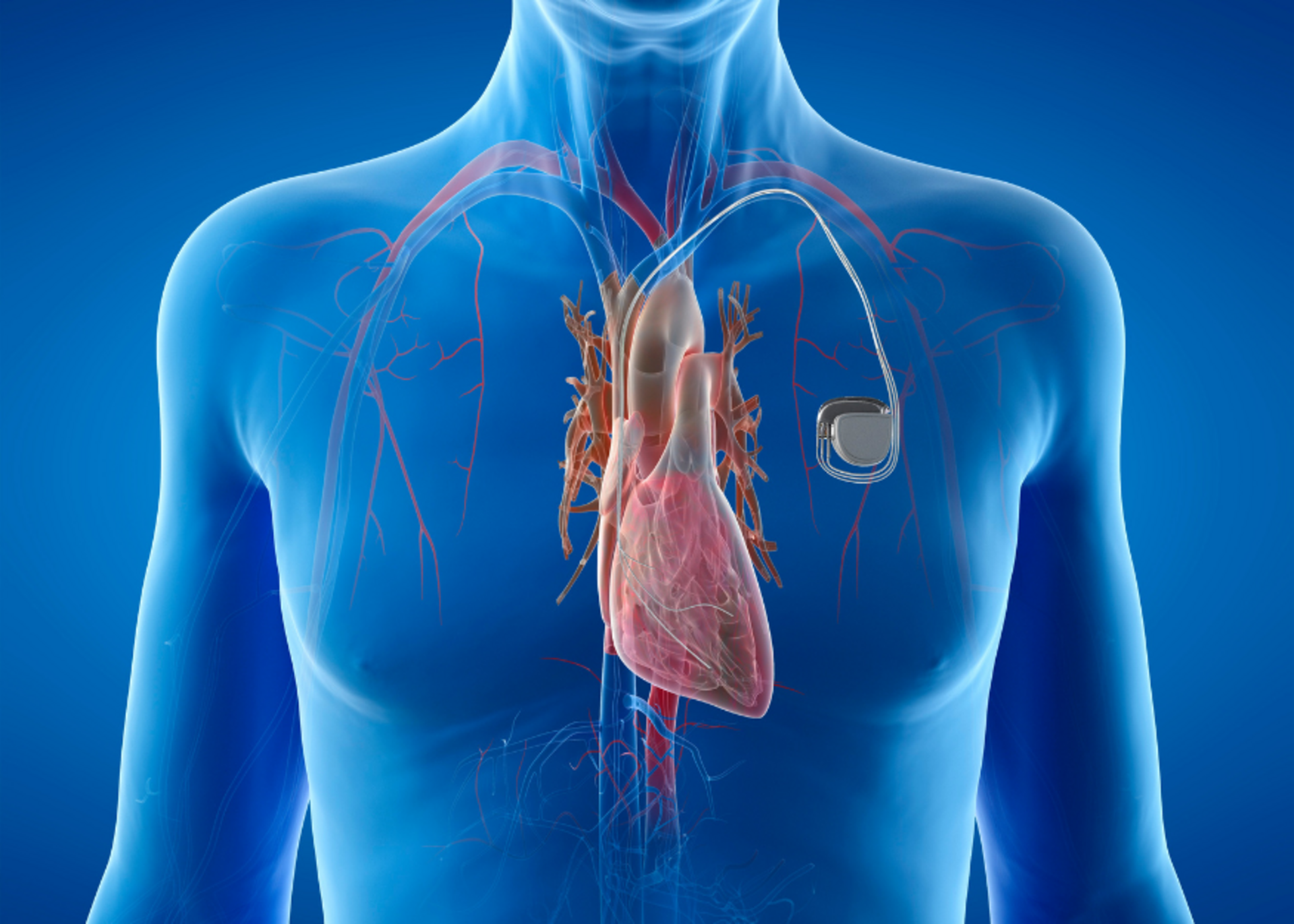
A pacemaker is a small, battery-operated medical device implanted under the skin near the chest. It helps regulate slow, irregular, or paused heartbeats (a condition known as bradycardia). It does so by sending electrical impulses to stimulate the heart and restore a normal rhythm.
Pacemakers are typically recommended for patients whose heart beats too slowly or irregularly, leading to fatigue, dizziness, fainting spells, or shortness of breath.
Why Might You Need a Pacemaker?
Pacemakers are usually advised for patients with:
Bradycardia (abnormally slow heart rate)
Heart block (a delay or interruption in the electrical signal transmission)
Atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular response
Post-heart attack or after certain cardiac surgeries
Advanced heart failure (in select cases requiring cardiac resynchronization)
These conditions may prevent the heart from pumping enough blood to meet the body’s needs. A pacemaker ensures that the heart beats at the right pace to maintain proper blood circulation.
How Does a Pacemaker Work?
A pacemaker consists of two main parts:
Pulse Generator – Contains the battery and electronic circuits that control the heartbeat.
Leads (Wires) – Deliver electrical impulses from the generator to the heart muscle.
Some modern pacemakers are leadless and directly implanted into the heart via a catheter-based procedure. These are suitable for select patients and reduce the risk of lead-related complications.
The pacemaker continuously monitors the heart rhythm. When it detects a slow or missed beat, it sends a mild electrical signal to prompt a normal contraction.
Types of Pacemakers
There are different types of pacemakers depending on the heart’s condition:
Single-Chamber Pacemaker: Sends signals to one chamber, usually the right ventricle.
Dual-Chamber Pacemaker: Coordinates activity between the right atrium and right ventricle.
Biventricular Pacemaker (CRT Device): Used for heart failure patients to synchronize contractions of both ventricles.
Pacemaker Implantation Procedure
Pacemaker implantation is a minimally invasive and relatively safe procedure, typically performed under local anesthesia.
A small incision is made near the collarbone.
The leads are guided through a vein into the heart under fluoroscopic (X-ray) guidance.
The pulse generator is placed under the skin and connected to the leads.
The incision is closed, and the pacemaker is programmed to suit the patient’s heart rhythm.
Most patients are discharged within 24 hours and can resume light activities within a few days.
Life After a Pacemaker
Having a pacemaker is not the end of your active life. With proper care and follow-up, most patients lead normal, productive lives.
Key post-implantation guidelines include:
Avoiding heavy lifting or vigorous arm movements for a few weeks
Regular follow-ups to monitor battery life and pacemaker function
Avoiding strong magnetic fields or devices that may interfere with the pacemaker
Carrying a pacemaker ID card at all times
Most pacemaker batteries last 7–10 years, after which the device may need replacement.
When Should You See a Cardiologist?
If you or a loved one experiences:
Frequent dizziness or lightheadedness
Fainting spells
Persistent fatigue without clear cause
Irregular or very slow heartbeats
Shortness of breath during mild exertion
it may be time to consult a cardiologist to evaluate your heart rhythm.
A pacemaker can be a life-changing solution for those with abnormal heart rhythms. It restores not just heart function but also confidence, energy, and overall quality of life. If you're facing symptoms of an irregular heartbeat or have been advised to consider a pacemaker, consult Dr. Mehul Rathod – Interventional Cardiologist in Latur – for expert advice and advanced cardiac care.
Read More:
Post-Heart Attack Treatment Guide by Dr. Mehul Rathod