Heart diseases remain one of the leading causes of death worldwide, and blocked arteries are often at the core of most cardiac emergencies. Among the various treatment options, coronary angioplasty stands out as a minimally invasive, highly effective procedure that helps restore blood flow to the heart. As a Consultant Interventional Cardiologist in Latur, Dr. Mehul Rathod brings expertise and precision to this crucial heart-saving intervention.
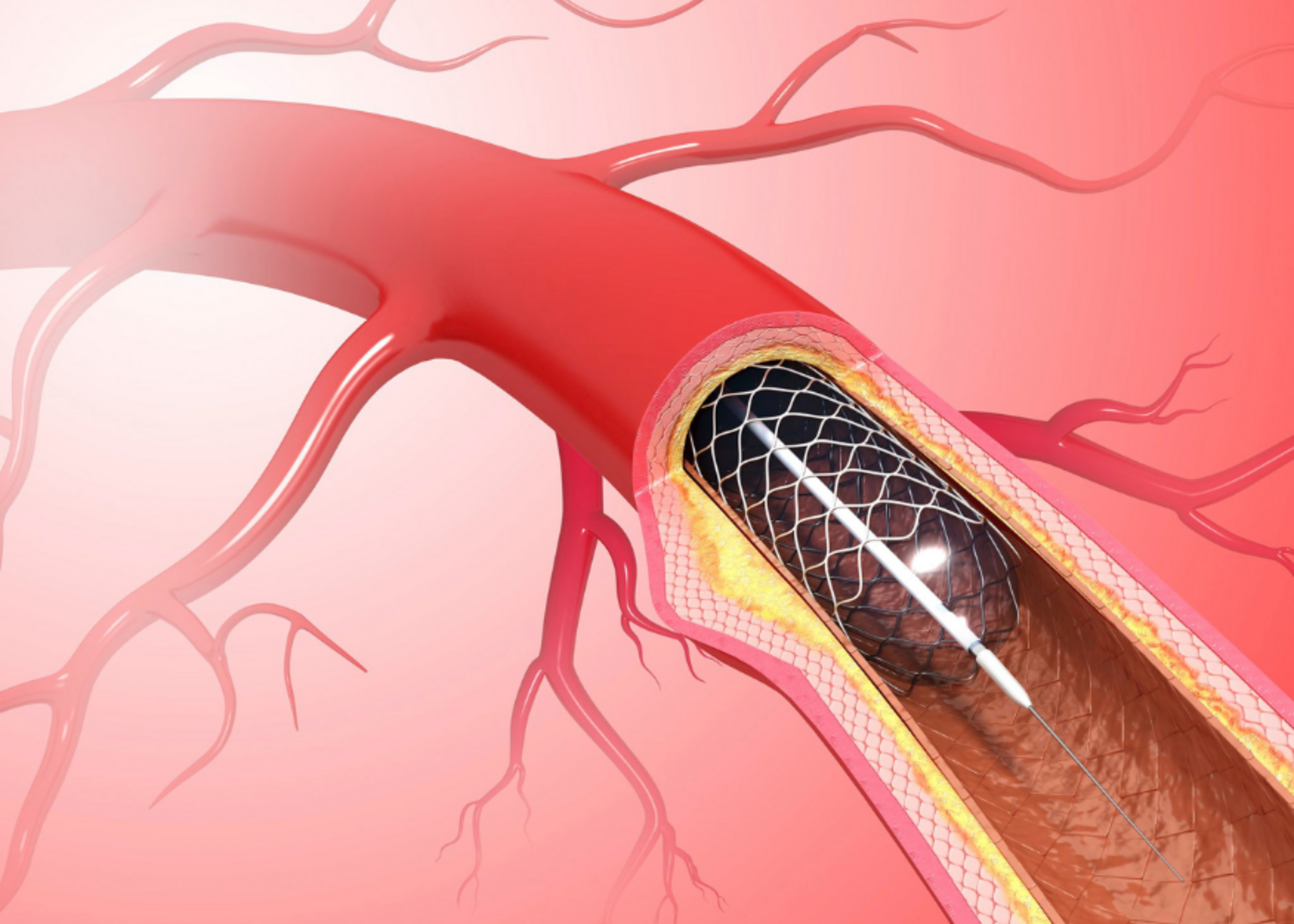
What is Coronary Angioplasty?
Coronary angioplasty, also known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), is a procedure used to open narrowed or blocked coronary arteries. These arteries supply blood to the heart muscle, and blockages can lead to chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, or even a heart attack.
During angioplasty, a small balloon is inserted into the blocked artery and inflated to widen the artery. In most cases, a stent (a small wire mesh tube) is then placed to keep the artery open long-term.
When is Coronary Angioplasty Recommended?
Dr. Mehul Rathod may recommend angioplasty in the following scenarios:It is particularly useful in emergency settings where time is critical to prevent irreversible damage to the heart muscle.
How is the Procedure Performed?
Coronary angioplasty is typically performed in a catheterization lab (cath lab). Here's a step-by-step overview:The entire procedure usually takes 30–60 minutes, depending on the number of blockages.
Recovery After Angioplasty
Most patients recover quickly after angioplasty and may be discharged within 24 to 48 hours, especially if no complications arise. Dr. Mehul Rathod advises the following post-procedure care:Coronary angioplasty is a vital procedure that can significantly improve symptoms and reduce the risk of heart attacks in patients with coronary artery disease. Early diagnosis and timely intervention can make all the difference.
If you’re experiencing chest discomfort, fatigue, or shortness of breath, consult Dr. Mehul Rathod, leading Interventional Cardiologist in Latur, for expert cardiac evaluation and care.